Learn the Fundamentals of Microbiology
Develop a better understanding of:
 Human Health
Human Health- Veterinary Health
- Food Processing and Management
- Horticulture
- Agriculture.
Microbiology is an increasingly important area of science; not only because of its obvious significance to human health, but also its significance to environmental management, veterinary care, farming and horticulture.
- Microbes have the potential to have a much greater impact upon cleaning up otherwise troublesome pollutants: everything from oil spills to plastics in the environment.
- Microbes can change the nature of soils, improving their ability to grow certain plants.
- Microbes can combat diseases in humans, animals and plants.
The application of microbiological knowledge is expanding along with advancement in microbiological research, but to understand the potential and apply yourself to the opportunities that are emerging you must first acquire a foundation in the subject. This is what this course sets out to do.
COURSE STRUCTURE
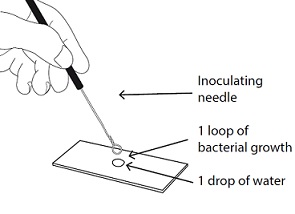
The course comprises 9 lessons as follows:
- Scope and Nature of Microbiology
- Microscopes
- Cultures
- Microbial Taxonomy
- Bacteria
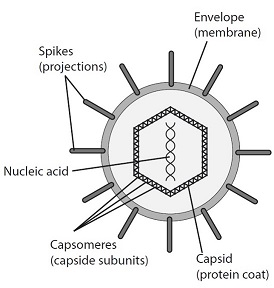
- Viruses
- Other Microbes - Protists, Fungi, Helminths
- Immunology
- Applied Microbiology
WHY DO WE STUDY MICROBES?
We often call micro-organisms ‘germs’ giving them the connotation of being something bad, but in reality, there are many microorganisms that benefit man and the environment we live in.
Differentiating between the good and bad is not always that straight forward, but it is important to recognise the benefits of microorganisms just as much as to recognise the problems they create. This is because even though bad microorganisms can be controlled by killing all microorganisms – to kill all would involve also removing microorganisms that we need.
Good Things Micro-organisms Do
Micro-organisms are responsible for the following:
- Facilitating digestion - of food we eat, and food that nourishes all animal and plant life.

- Keeping us healthy - good microbes protect us from pathogens by colonising our bodies so that there is less room for bad microbes to invade. They can also boost our immune system helping us fight diseases such as cancers and protecting us against auto-immune diseases. They digest our food and help us to stay slim by producing chemicals in our bodies that improve our metabolic rate. They detoxify our system and metabolise toxins that might otherwise be harmful to us.
- Helping plants grow - legumes form special nodules on their roots. In these nodules live Rhizobium bacteria which take up freely available nitrogen gases from the air and use it for their own growth. In addition, the bacteria convert large amounts of atmospheric nitrogen which they do not need into a form that the legumes can use. The bacteria provide large quantities of nitrogen for the legume while the legume provides a home and some nutrients for the bacteria. This sort of mutually helpful partnership is called a symbiotic relationship.
- Some beneficial fungi grow in a symbiotic relationship with the root cells of higher green plants. This is termed a mycorrhizal association. Roots of many cultivated plants including corn, soybeans, cotton, tobacco, peas, red clover, apples, citrus, pines, eucalypts and others have mycorrhizal relationships with higher fungi. The mycorrhizae appear to be highly beneficial for optimal growth of many plants. Establishing proper mycorrhizal fungi with cultivated plants offers a great potential for improved plant growth. Some mycorrhizae form a kind of sheath around the roots sometimes giving a hairy or cottony appearance. The plant roots transmit substances to the fungi and the fungi aid in securing and transmitting nutrients and water for the plant roots. Because they provide a protective cover, mycorrhizae increase the plant's tolerance to drought, high temperatures, infection from disease fungi and even to extreme soil acidity and are able to improve the efficiency of nutrient absorption. Mycorrhizae grow and develop best in a well aerated soil in a sunny position. High application of nutrients tends to inhibit their development. The greatest growth responses to mycorrhizae are likely to occur in highly weathered soils which are low in basic cations and are low in phosphorus.
- Producing special effects - like variegation in plants (viruses).
 Decomposing waste materials - including human effluent, all sorts of plant and animal waste, cleaning up oil spills and decomposing other things such as plastics (Note -even though decomposition of plastics may be slow, it does nevertheless occur) and nylon.
Decomposing waste materials - including human effluent, all sorts of plant and animal waste, cleaning up oil spills and decomposing other things such as plastics (Note -even though decomposition of plastics may be slow, it does nevertheless occur) and nylon.- Making bio fuels - such as ethylene by consuming and decomposing waste (including human waste) plus toxic waste and turning it into electricity. Geobacter bacteria even consume radioactive waste (immobilising materials such as uranium).
- Metabolising methane - methane is produced through all sorts of industrial activity and some bacteria can use copper (a potentially toxic heavy metal) from the environment to metabolise methane this may be one answer to green-house gases and global warming.
- Producing fermented foods including wine, beer, cheese, pickles, yoghurt and many other important food products.
How Can This Course Benefit You?
 Microbiology impacts on your life in more ways than you can imagine.
Microbiology impacts on your life in more ways than you can imagine.
- Understanding microbiology will enable you to see possibilities in both your personal and work life which you may otherwise have missed.
- This course can enhance career, work and business opportunities in more industries than you might begin to imagine (until after you complete the course).
Microbiology is a big part of the future in not only life sciences, but much more.
- It allows us to understand things that occur beyond the naked eye - inside our bodies, in our environment, on farms and in gardens, and in the air, soil and water around us.
- Microbiological knowledge underpins so many of the world's recent breakthroughs across a wide range of industries. It is helping us to understand human, animal and plant diseases in ways we couldn't have imagined a few decades ago. Similarly, we now understand more about human nutrition, how to handle food better and what happens to things we eat inside the body. We can understand the microscopic dynamics of what causes plants to grow or decline; and much, much more.
Microbiology affects everyone in so many ways; and this course provides a foundation for beginning to understand how.
HOW THE COURSE WORKS
You can start the Microbiology course at any time. You study by distance learning, which gives you the flexibility to choose when and where you study.
Students are supported in their studies by our highly qualified and friendly tutors. They are there to provide guidance and support every step of the way. If you have any questions at all, they are always happy to help.
START YOUR STUDIES
It's easy to enrol - just go to the top of this page, select your payment plan and study method.
If you have any questions about the Microbiology course, or any ACS courses, please get in touch with us today - connect with our specialist Science tutors. Discuss your goals and different study options. We will be pleased to hear from you!